
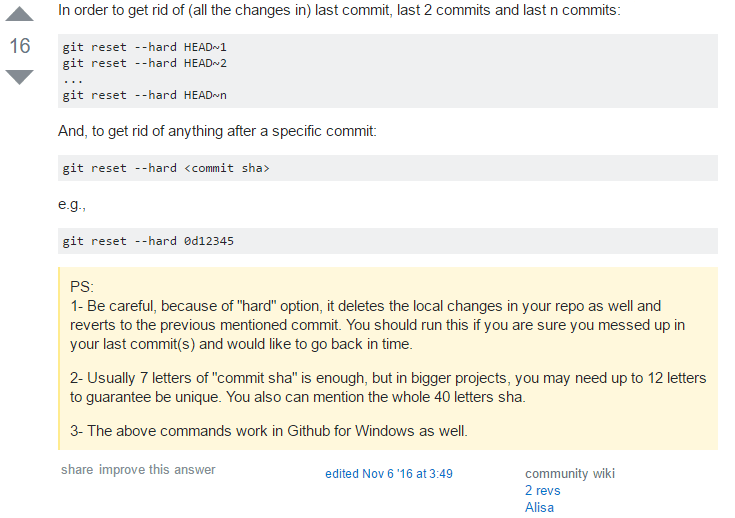
First, it doesn’t change the project history, which makes it a “safe” operation for commits that have already been published to a shared repository. Reverting has two important advantages over resetting. In Git, this is actually called a reset, not a revert. It's important to understand that git revert undoes a single commit-it does not "revert" back to the previous state of a project by removing all subsequent commits. These are the other trees Git uses to manage the state of the repository. Instead of creating the new commit this option will add the inverse changes to the Staging Index and Working Directory. Passing this option will prevent git revert from creating a new commit that inverses the target commit. With the repo in this state, we are ready to initiate a git revert. At the end of the repo setup procedure, we invoke git log to display the commit history, showing a total of 3 commits. We have made 3 commits to the repo in which we have added a file demo_file and modified its content twice. Here we have initialized a repo in a newly created directory named git_revert_test. Initialized empty Git repository in /git_revert_test/.git/ $ touch demo_file $ git add demo_file $ git commit -am"initial commit" initial commit 1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 demo_file $ echo "initial content" > demo_file $ git commit -am"add new content to demo file" add new content to demo file n 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) $ echo "prepended line content" > demo_file $ git commit -am"prepend content to demo file" prepend content to demo file 1 file changed, 1 insertion(+) $ git log -oneline 86bb32e prepend content to demo file 3602d88 add new content to demo file 299b15f initial commit $ mkdir git_revert_test $ cd git_revert_test/ $ git init . To demonstrate let’s create an example repo using the command line examples below: The ref pointers are then updated to point at the new revert commit making it the tip of the branch. A revert operation will take the specified commit, inverse the changes from that commit, and create a new "revert commit". Git revert also takes a specified commit, however, git revert does not move ref pointers to this commit. Other 'undo' commands like, git checkout and git reset, move the HEAD and branch ref pointers to a specified commit. The git revert command is used for undoing changes to a repository's commit history. Instead of manually going in, fixing it, and committing a new snapshot, you can use git revert to automatically do all of this for you. This can be useful, for example, if you’re tracking down a bug and find that it was introduced by a single commit. Reverting should be used when you want to apply the inverse of a commit from your project history.

This prevents Git from losing history, which is important for the integrity of your revision history and for reliable collaboration.
#Git undo commit after push to github how to#
Instead of removing the commit from the project history, it figures out how to invert the changes introduced by the commit and appends a new commit with the resulting inverse content. The git revert command can be considered an 'undo' type command, however, it is not a traditional undo operation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
